Acids and Base Equilibria
Acids and Base Equilibria
 Buffer Solutions resist chang in pH. A typical solution is made up by
mixing a weak acid with its conjugate base or a weak base with its conjugate
acid. The weak bases tends to neutralize any extra acid added to the buffer,
and the weak acid tends to neutralize any extra based added. However, with
enough acid is base the capacity of the buffer can always be overwhelmed.
Buffer Solutions resist chang in pH. A typical solution is made up by
mixing a weak acid with its conjugate base or a weak base with its conjugate
acid. The weak bases tends to neutralize any extra acid added to the buffer,
and the weak acid tends to neutralize any extra based added. However, with
enough acid is base the capacity of the buffer can always be overwhelmed.
Take for example a buffer when a weak acid HA mixed with its conjugate base in
the form of NaA in water.
HA(aq) + H2O(l) <==> H3O+(aq) + A-(aq)
As long there is an appreciable amounts of the weak acid and its conjugate
base, the hydronium ion concentration is
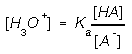
The concentration ratio, not the concentration governs the hydronium
ion concentration. If more acid or base is added the ratio changes slightly
and keeps the buffer at near its buffered pH.
If either of the [HA] or [A-] goes to zero, the ratio goes to
zero or infinity, and the equation describing the buffer loses its meaning.
Buffer action no longer occurs. Both acid and conjugate base must be
present for buffer action.
If we consider a buffer when a weak base B is placed into solution with
with its conjugate acid,
B(aq) + H2O(l) <==> HB+(aq) + OH-(aq)
we can calcuate the buffered contration of hydroxide ion,
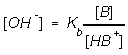
 Strong Acid-Base titration is a procedure for determining the amount of an
acid or base in solution. During a titration, acid and base are mixed in a controlled
fashion. The progress is follwed by measuring the pH of solution as a function
of titrant (whats added). See Figures 6-9 and 6-10 for typical examples.
Strong Acid-Base titration is a procedure for determining the amount of an
acid or base in solution. During a titration, acid and base are mixed in a controlled
fashion. The progress is follwed by measuring the pH of solution as a function
of titrant (whats added). See Figures 6-9 and 6-10 for typical examples.
Consider the titration of a strong acid, HCl, with a strong base, NaOH. In soultion
the neutralization reaction is
H3O+(aq) + OH-(aq) <==> 2 H2O(l)
At the starting point, no titrant has been aded. The H3O+(aq)
concentration equals the concentration of the strong acid.
As the reaction approaches equivalence, some base has been added. Assuming
that any bases that has been added neutralizes the same amount (mols) of acid, the
concentration of H3O+(aq) is the remaining of moles acid
divided by the total volume.
At the equivalence point, the amount of base and acid are exactly equal. The
only concentration of H3O+(aq) comes from the autoionization
of water. The pH is then 7.0.
Beyong the euaivalence point more base has been added then is neccessary to
neutralize all the acid. The excess strong base would give rise to OH-(aq)
Titration of a weak acid with a strong base has the same four regions. However there is an
equilibrium associated with such a problem. See problem 6-45.
 Weak Acid/Strong Base Titration
Weak Acid/Strong Base Titration
Consider the titration of a weak acid with a strong base. At the starting point
there is only the weak acid. The concentration of H3O+ is in
equilibrium with the weak acid. We can calculate the concentration of solutes if we know the
Ka and the amount of weak acid at the starting point.
Between the starting point and the equivalence point we have a buffer solution.
The titrant (strong base) has neutralize some of the weak acid and formed it conjugate base.
We can calcualte the equilibrium concentration using the equations that describe buffer
solutions (see above).
At the equivalence point, moles of acid equals moles of base. All the weak acid has been
converted to its conjugate base. The conjugate base wants H+ and extracts it from water
producing some weak acid and hydroxide ion. We can calculate the equilibrium concentrations, knowing
Kb.
After the equivalene point, moles of base overwhelms the buffer and the excess added
hydroxide ions dominate.
 Polyprotic Acids contain two or more H atoms that can dissociate. For example
H2SO4 is a diprotic acid and H3PO4 is a triprotic
acid. Polyprotic acids donate hydrogen ion in stages with the first stage dominating the latter stages.
Polyprotic Acids contain two or more H atoms that can dissociate. For example
H2SO4 is a diprotic acid and H3PO4 is a triprotic
acid. Polyprotic acids donate hydrogen ion in stages with the first stage dominating the latter stages.
The first protonation (Ka1 is typically 10,000 times greater than the second.
Most the the hydrogen ion in solution comes from the first stage.
At high pH, most of the concentration of a polyprotic acid will be in the form of the most negative conjugate base.
At low pH, the more acidic (higher Ka) form of the poluprotic acid will exist.
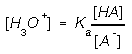
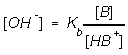
 Buffer Solutions resist chang in pH. A typical solution is made up by
mixing a weak acid with its conjugate base or a weak base with its conjugate
acid. The weak bases tends to neutralize any extra acid added to the buffer,
and the weak acid tends to neutralize any extra based added. However, with
enough acid is base the capacity of the buffer can always be overwhelmed.
Buffer Solutions resist chang in pH. A typical solution is made up by
mixing a weak acid with its conjugate base or a weak base with its conjugate
acid. The weak bases tends to neutralize any extra acid added to the buffer,
and the weak acid tends to neutralize any extra based added. However, with
enough acid is base the capacity of the buffer can always be overwhelmed.