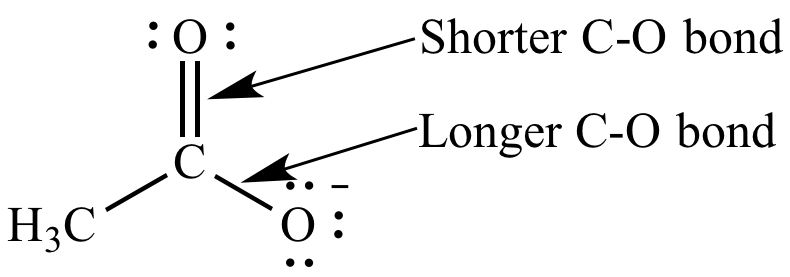
The resonance
hybrid (derived from several resonance
contributors) explains the equal C-O bond
lengths:
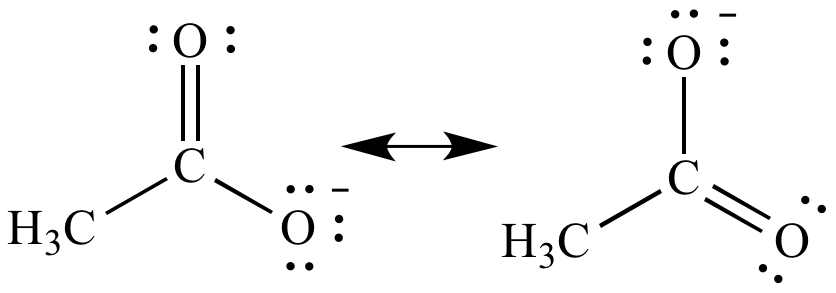
Resonance contributors



| Orientation of applied magnetic field (B0) |
Add energy (excitation) Release energy (relaxation) |
|||
| I = + 1/2 Lowest energy Ground state |
I = - 1/2 Higher energy Excited state |