
Combustion of methane is an oxidation because there is an increase (from zero to four) in number of bonds between carbon (EN = 2.5) and oxygen (EN = 3.5).

Free radical halogenation of methane is an oxidation because there is an increase (from zero to one) in the number of bonds between carbon (EN = 2.5) and bromine (EN = 2.8).
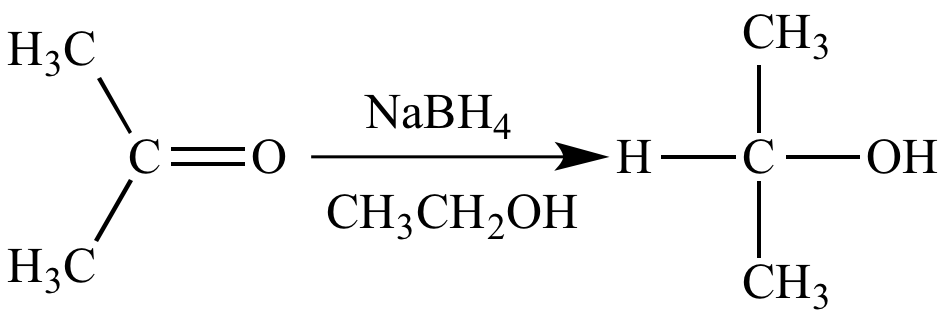
Reaction of sodium borohydride with acetone is a reduction because there is an increase (from zero to one) in the number of bonds between carbon (EN = 2.5) and hydrogen (EN = 2.1), and also between oxygen (EN = 3.5) and hydrogen (EN = 2.1).

Catalytic hydrogenation of propene is a reduction because there is an increase (from three to five) in the number of bonds between carbon (EN = 2.5) and hydrogen (EN = 2.1).