a. The epoxidation of 1,2-dihydronaphthalene (using bleach and Jacobsen’s catalyst) affords high ee-values (~85%) while the one for cis-stilbene (Ph-CH=CH-Ph) leads too much lower ee-values (~50%). Explain briefly.
b. Suggest two ways to improve the stereoselectivity of an epoxidation reaction from alkenes?
2. (30 points) A student performs an epoxidation of styrene. The GC/MS spectrum of her compound is shown below. Show all your work.
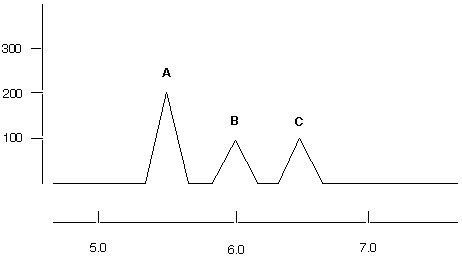
a. Assuming that all three compounds have the same response factor, determine the relative percentages of A, B and C in the mixture.
b. Assuming that the peaks A and B can be assigned to the different epoxide products, calculate the ee value for this reaction.
c. How can you account for the peak C? Show appropriate mechanism for its formation using the correct structures.
d. What column was used to separate the two forms of styrene oxide? Which one has usually the shorter retention time?
3. (25 points) Drying of solvents
a. Which drying agent would you use to dry the following solvents? Show pertinent chemistry.
A. Tetrahydrofuran
B. Dichloromethane
C. Acetonitrile
b. Why should you use drying agents like anhydrous sodium sulfate sparingly?
c. Which of the following drying agents has the highest capacity: Na2SO4, CaSO4 or MgSO4? How many water molecules can this compound absorb per molecule of drying agent?
4. (30 points) A researcher has the task to isolate (S,S)-Diaminocyclohexane (MW=114 g/mol) from the mixture of Diaminocyclohexanes commercially available (60% trans : 40% cis).
a. He decides to use tartaric acid (MW=150 g/mol) for this task. Since his laboratory is well funded, he can located three forms: L-(+), D-(-) and DL. Which one should he choose? Justify your answer.
b. How can he determine if his resolution was successful? Propose two independent methods of evaluation and explain briefly how they work.
c. He starts his reaction with 5.7 g of the mixture. Assuming he has quantitative yield, how many grams of the product does he isolate? Show your work.
5. (35 points) Predict the major products of the following reactions. Show correct stereochemistry.
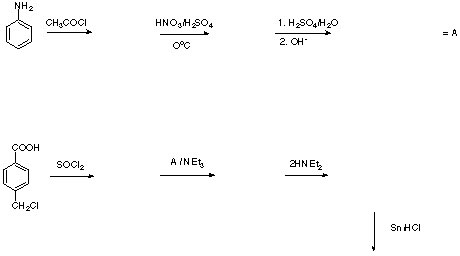
6. (35 points) Referring to the Grignard reaction, answer the following questions. Show pertinent chemical equations when appropriate.
a. Why is it important to add the bromobenzene solution slowly?
b. Why do you use PhBr instead of PhI even though the reaction with Mg requires a little more rigorous conditions?
c. Why is it a good idea to scratch or break up the magnesium turnings before you place them in reaction vessel? Explain briefly.
d. Grignard reagents underly the Schlenk equilibrium. Provide the chemical equation showing the compounds present in this equilibrium. Which technique allows you to show their presence? Which fact complicates the analysis of these spectra?
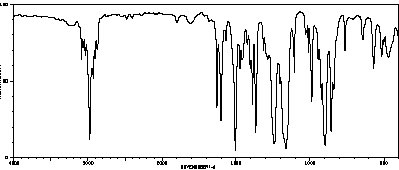
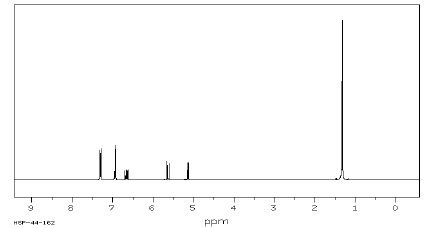
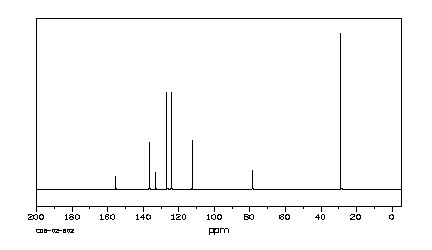
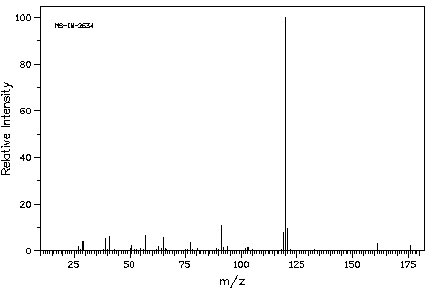
7. (25 points) Compound Z has a molecular formula of C12H16O. Based on the spectra given below, suggest a structure for compound Z. Credit is given only for analysis work shown.
a. Calculate the degree of unsaturation.
b. Assign four pertinent peaks in the IR spectrum.