3. excess acetic andydride was used +2 points
easier to remove + 4 points
acetic anhydride decomposes in water to water soluble acetic acid.
4.
ANSWER KEY
1. the reagent used in least molar amount relative to what is theoretically required + 5 points
or the compound which is less than the stoichiometric amount required
or the chemical which prevents the reaction from going on any further
and chemical equation from lab or lecture notes needed for full credit. + 5 points
2. 13C NMR means carbon proton coupled and 13C{1H} is proton decoupled +4 points
e.g., (other examples are possible)
| 13C | 13C{1H} | |
| CH2 | singlet | triplet |
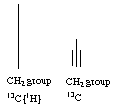
3. excess acetic andydride was used +2 points
easier to remove + 4 points
acetic anhydride decomposes in water to water soluble acetic acid.
![]() +4 points
+4 points
4.
a. moles of diprotic acid = 0.530 g / (166.13 g/mol) = 3.19 mmol
moles of acidic protons = 2 x 3.19 mmol = 6.38 mmol
volume of NaOH needed = (6.39 mmol) / (0.240 mol/L) = 2.66 x10-2 L = 26.6 mL
work is worth 5 points
- 2 points if in Litre
- 2 points if ± 0.2 or if only 2 or 4 significant figures.
b. mw = 0.1799 g / (13.90x10-3L x 0.106 mol/L) = 122 g/mole or 1.22 x102 g/mole
5. The nitrile peak is more intense since it would have the greater net dipole change during the vibration (stretching).
- 2 points if "net" is not mentioned.
6. 3 points each (no partial credit)
| 4 | 6 |
| 5 | 11 |
7. a. C16H16; unsat # = 9 (no partial credit)
b. 3 (no partial credit)
8. E, A, C, H, D
9. Ultimately, to determine the moles of Iron present (or to determine the concentration (mol/L) of iron in your sample product).
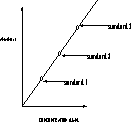
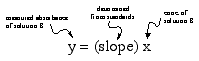 solve for x!
solve for x!
10. a. solute - a substance dissolve in a solvent
b. eluant - the solvent (that is passed through the column)
c. mobile phase - the solvent
d. stationary phase - the resin (the phase in which the sample is adsorbed on or the phase that the sample interacts)
11. The compounds need to associate (interact) with the stationary phase for separation to occur. +4 points
Using the "like-dissolve-like" rule, a nonpolar compound would not associate with (dissolve in) the stationary phase. + 4 points
12. it would increase the retention time
or would double the retention time (acceptable though not fully accurate)
13. a. C1 = 1000 mg/46 mL
C2 = 1000 mg/5.5 mL
K = C2/C1 = 46/5.5 = 8.36 = 8.4
b and c.
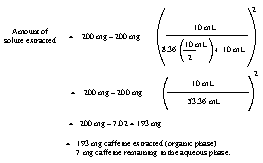
14.
11.78 mL x 0.01052 M = 1.239x10-4 moles EDTA
0.2481 g / 20 = 0.01240(5) grams
mw of marble = (0.012405 g) / (1.239x10-4 moles) = 100.1 g/mole
15.
1) sample is vaporized (sample chamber, under vacuum)
2) sample is passed through ionizing beam - fragmentation
3) ions are accelerated (acceleration plates)
4) ion are passed through a magnetic field
5) detector - based on mass to charge ratio.
16.
a) 134 peak
b) ![]()
c) 91
d) ![]()
e) M+1 peak which is 12C813C11H1016O1