
Electrophilic aromatic substitution
The following diagram show the different possibilities of stabilization of the positive charge in the transition state.
Note that the ortho and para-attack have one more resonance form that can contribute significantly if the attached
X-atom is electron-donating (e.g. has a lone pair).

Here are a few examples of how the first substituent can direct the incoming electrophil into a specific position.
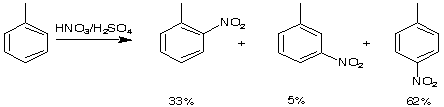
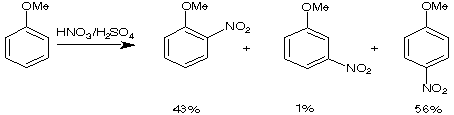
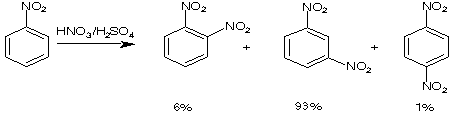
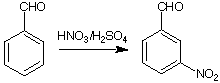 75-84%
75-84%
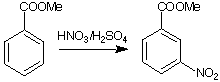 81-85%
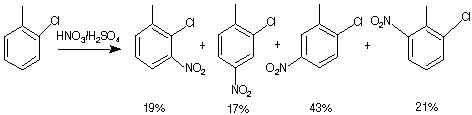
81-85%
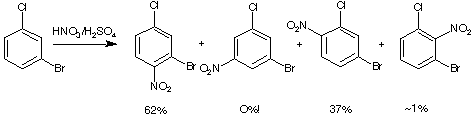
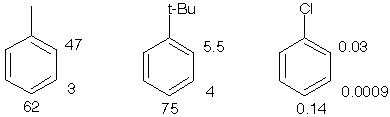
Partial speed of nitration (in reference to benzene)
Directing effects
ortho/para directing, activating: R(alkyl), -NH2, -NR2, -NHCOR, -OH, -OR, OCOR
ortho/para directing, deactivating: halogene
meta directing, deactivating: -NO2, -SO3H, -CCl3, -CF3, -COOH, -COOR, -CHO, -COR
Nitration reagent
1. diluted or concentrated HNO3
2. Mixture of concentrated HNO3 and H2SO4
3. Nitronium salts (NO2+BF4-, NO2+PF6-)
4. N2O5 in CCl4 (NO2+ + NO3-)
Planning of a synthesis:
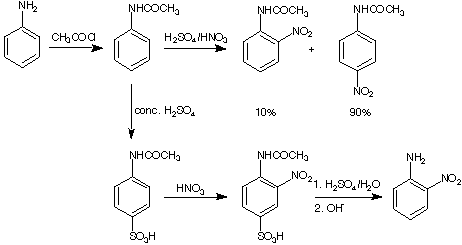
Question: How do you obtain the meta-nitroaniline?