last updatedThursday, January 14, 2016
Meeting 4 (Condensed Key)
1. a. The ligand and manganese(II) acetate dissolve poorly in
95 % ethanol at room temperature. The initial reflux serves the purpose
getting both in solution and to form the Mn(II) salen complex.
b. The crushing of the manganese(II) acetate increases its surface
area, which allows for the salt to dissolve faster in 95 % ethanol
faciliting the formation of the Mn(II) salen complex. This step is important
to reduce the formation of MnO2 caused by the oxidation of
Mn(II) in the absence of the ligand. MnO2 is a thermodynamic
trap, which means that once it is formed, the catalyst cannot form
anymore.
c. The proper reflux is necessary to bring the ligand and
manganese(II) acetate gradually in solution to form the Mn(II) salen
complex. The student should observe that (i) the solution boils (ii) a
reflux ring is observed in the low third of the condenser and (III) the
ligand gradually dissolves.
d. The color will change from bright yellow to dark-brown and the entire ligand should dissolve as the reaction proceeds.
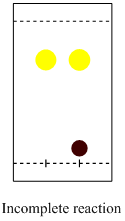
e. Silica is used as stationary phase and a mixture ethyl
acetate:hexane (1:4) as the mobile phase. The incomplete reaction shows
two spots in the lane for the reaction mixture, the ligand (Rf= ~0.8) and the
precursor to the catalyst (Rf= ~0.1).

f. Ethanol dissolves in water and ethyl acetate, which will cause problems during the extraction because emulsions are more likely to form. Thus, the amount of ethanol should be reduced as much as possible.
g. The extraction with saturated sodium chloride solution aims to remove the bulk of the water and residual ethanol from the organic layer.
h. The solution should be as concentrated as possible before adding
the high-boiling petroleum ether (hbPE, =mixture of
hydrocarbons). The addition of high-boiling petroleum ether lowers the polarity of the solution, which facilitates the
precipitation of the catalyst as the ethyl acetate is slowly removed
from the mixture using the rotary evaporator.
i. The weakly polar ligand
and the aldehyde remain in solution in h.. If the solvent was completely
removed, the catalyst, the ligand and the aldehyde would be co-mingled in
the solid.