last updatedWednesday, November 04, 2015
Meeting 12 (Condensed Key)
1. a. Acetic acid anhydride is used as carboxylic acid precursor in the reaction.
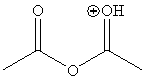
b. Concentrated phosphoric acid (85 %) is used as catalyst in this reaction. Note that most of the literature proposes that the carbonyl group is protonated because the resulting cation is resonance-stabilized. Some older literature claims that the oxygen in the bridge is protonated generating acetic acid as a leaving group.

c. Despite the addition of the catalyst, the reaction is still slow at room temperature. In order to establish the equilibrium faster, the reaction mixture is heated to 80 oC. An increase from 20 oC to about 80 oC will increase of the reaction by a factor of about 60, the difference between about 1.5 % conversion or 90 % conversion (theoretically).
d. The reaction mixture is added to cold water in order to precipitate the ester and the phenol. The catalyst, the acetic acid and the anhydride remain dissolved in water.
e. 95 % ethanol is used as solvent for the recrystallization. The ester is less polar than the starting phenol, which causes the ester to precipitate first.
2. a. The nitronium ion is a very powerful electrophile because there is only one "good resonance structure", in which the nitrogen atom bears the bulk of the positive charge.
b. The electrophile is obtained by the reaction of magnesium nitrate and glacial acetic acid. The acetyl nitrate (CH3COONO2) formed decomposes at higher temperatures producing the nitronium ion (and an acetate ion).
c. The nitro compound is supposed to precipitate while the magnesium salts, the acetic acid and the nitric acid remain in solution. It is important to use ice here to reduce the hydrolysis of the ester.
d. The crude contains different stereoisomers of the nitration products of the ester since there are several possible positions (4', 2' or 2-nitro). In addition, there could also be some nitro phenols if the ester function was hydrolyzed during the reaction.
e. The crude is recrystallized from absolute methanol. Any aqueous solutions have to be avoided to prevent hydrolysis of the ester.