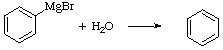 +
MgBr(OH)
+
MgBr(OH)
last updatedWednesday, February 11, 2015
Meeting 11 (Condensed Key)
1. a. Grignard reagents are very strong bases that react with anything that contains acidic protons i.e., water. The byproduct of the reaction, MgBr(OH), is insoluble in diethyl ether and coats the Mg-surface which prevents the formation of any new Grignard reagent.
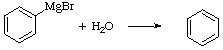 +
MgBr(OH)
+
MgBr(OH)
The water is introduced in the reaction through the "wet" glassware (which is silica based and therefore polar), the reagents and the solvent, which is hygroscopic, and moisture in the air that is absorbed by the glassware and the solvent. The glassware is dried with a heat gun prior to use, anhydrous diethyl ether is used, the reagent bottles should be kept close and the reaction setup is only allowed to "breathe" through a drying tube.
b. The mixture first turns milky, then greenish and finally brown. In addition, the mixture should start to boil because the formation of the Grignard reagent is exothermic.
c. The two-necked (or three-necked) flask is heated with a warm water bath (not directly on the hotplate or with a heat gun).
d. The addition of the ethereal bromobenzene solution has to be carried out in a way that the reaction maintains a gentle boil. A slow addition also reduces the temperature in the reaction and suppresses the formation of biphenyl because the formation of the Grignard reagent is favored at lower temperatures. If he added the solution too rapidly, the reaction mixture would foam very heavily and turn dark brown. Ultimately, he will not isolate much benzoic acid because a lot of the Grignard reagent is consumed otherwise.
PhMgBr + PhBr ------> Ph-Ph + MgBr2
e. Dry ice is solid carbon dioxide, which is very cold (~ -80 oC). Its reaction with the Grignard reagent yields the benzoate. It cannot be touched directly (transferred with a scoop or other tool) and should only be handled in open containers due to the evaporation at room temperature. It should be weight right before it is needed to reduce the condensation of moisture.
f. The addition of concentrated sulfuric acid converts the carboxylate to benzoic acid. The addition of chipped ice (=solid H2O) aim to control the temperature and to prevent the evaporating of the diethyl ether. After the ice melted, it will also serve as solvent for the Mg-salts.
PhCOO- MgBr+ + H+ ----- > PhCOOH + Mg2+ + Br-
g. The treatment of the combined organic layers with sodium hydroxide causes a deprotonation of benzoic acid and its transfer into the aqueous layer as benzoate. The unreacted bromobenzene, the biphenyl and most other organic compounds that are not acidic remain in the organic layer.
PhCOOH + OH- ----> PhCOO- + H2O
h. The aqueous extract in g. is acidified with hydrochloric acid. The product that precipitates from the solution is isolated by vacuum filtration, washed with water and dried.