exo product
cis-norbornene-5,6-exo-dicarboxylic acid
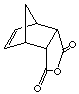
endo product
cis-norbornene-5,6-endo-dicarboxylic acid
Week 4 Problem Set - 30BL (Turn in your computer assignment during week 5)
PART I. DIELS ALDER RXN
This assignment is to be completed in the UCLA Science Learning Center computing labs.
1. You can download the files that you saved during the first computer assignment. Alternatively, the files you need for today's assignment can be found at the following location: (at the desktop level) double click the Network Neighboorhood icon --> Dellsrv2 --> Commonly Shared Folders. Copy the the 130AL folder to your desktop.
2. Optimize the above structural geometry of the below EXO and ENDO cycloadducts (see below instructions). Compare the heat of formation of the endo and exo cycloadducts. Which one is more stable product (thermodynamic product)? How can you rationalize the differences?
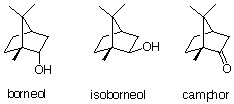
3. Optimize the above structural geometry of borneol, camphor and isoborneol. (see below instructions). Compare the heat of formation of borneol and isoborneol. Which one is more stable product (thermodynamic product)? How can you rationalize the differences?
4. Determine the dipol momentum for borneol, camphor and isoborneol. (see below instructions). In the GC spectrum, camphor has the shortest retention time, then isoborneol and borneol last. Can you rationalize the GC results based on the calculated dipole momenta of these compounds? (Note: The GC column is weekly polar.)
|
exo product cis-norbornene-5,6-exo-dicarboxylic acid |
 endo product cis-norbornene-5,6-endo-dicarboxylic acid |
 |
Instructions:
- Build, minimize and save the structure. (don't forget to Minimize the structure after building it!!)
this is the minimize button. Always minimize your structure before leaving the building mode.
- click on
to enter View Mode
- Select Calculations from the Setup menu.
The following window should appear. Select the options shown.
Verify the Charge is Neutral and Multiplicity is Singlet. Click OK.
- Select Submit from Setup menu.
- When the calculation is completed you will be notified.
- Select Output from the Display menu.
Record the heat of formation value given
See these Helpful Hints for manipulating structures!
Note:
| 1 au = 1 hartree = 627.5 kcal/mol |
| 1 eV = 23.06 kcal/mol |
| 1 hartree = 27.21 eV |
| 1 Ångstrom = 1.889762 atomic units = 10-8 cm |
3. Calculate the LUMO for maleic anhydride and cyclopentadiene (see below instructions). Compare and contrast the LUMO diagram of maleic anhydride given in the course reader from the one generated by PC Spartan Plus.
|
cyclopentadiene |
maleic anhydride |
Instructions:
- Build and save the structure. (don't forget to Minimize the structure!!)
- click on
to enter the View Mode
- Select Calculations from the Setup menu. The following window should appear. Select the options shown.
Click OK to close the window.
- Under the Setup menu, select Surfaces. A window should appear. In this window click Add.
A second window should appear. In this window, select the following
Then click OK to exit dialog. Close the previous window.
Select Submit from Setup menu. When the calculation is completed you will be notified.
- Under the Display menu, select Surfaces.
A window should appear. In this window check the yellow box.
Next, select the molecule by clicking on it. In the bottom right corner of the window, change the selection from Solid to Transparent.
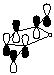 LUMO of maleic anhydride (from course reader) |
Draw the LUMO generated from PC Spartan Plus (or print and paste) |
4. Calculate the HOMO for cyclopentadiene. Compare and contrast the HOMO diagram of cyclopentadiene given in the course reader from the one generated by PC Spartan Plus.
Instructions:
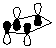 HOMO of cyclopentadiene (from course reader) |
Draw the HOMO generated from PC Spartan Plus (or print and paste) |
PART II. Aldol Experiment
1. a. Calculate the dipole moment for benzil, dibenzyl ketone and tetraphenylcyclopentadienone. Draw the structure and the net dipole. Which has the greatest dipole? Which has the smallest dipole? [During lab of week 6 you will TLC these three components. The dipole calculations performed here will help you determine their relative Rf values].
|
dibenzyl ketone |
benzil |
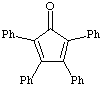 tetraphenylcyclopentadienone |
2.a. Calculate the dipole moment for Isoborneol, borneol and camphor. Based on these data, can you explain the sequence of peaks in the GC spectrum of the camphor experiment?
Instructions:
- Build and save the structure.
- click on
to enter the View Mode
- Select Calculations from the Setup menu. The following window should appear. Select the options shown.
Click OK to close the window.
- Select Submit from Setup menu. When the calculation is completed you will be notified.
- Under the Display menu, select Properties.
A window should appear (the values in this example should differ from yours). If there are no values in the window then you need to double click on the molecule.
Record the dipole moment given. (In this example the dipole = 3.9 debye).
PART III.
|
1. Calculate the dipole moment for dihedral angles: 0 through 180 degrees in 10 degree increments. Plot the dipole moment of benzil vs. the dihedral angle. |
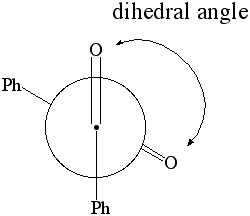
Newman Projection of Benzil |
Instructions:
- click on Constrain Dihedral angle tool,
- select the atoms shown below (i.e., both oxygens and and carbonyl carbons)
- Click on the lock tool,
, in the bottom right corner so that it looks like this,
- Set the dihedral angle to 0 and hit the ENTER key.
- click on the minimize tool,
, and wait for the operation to complete.
- click on the minimize tool,
, a second time and wait for the operation to complete.
- Select Calculations from the Setup menu. The following window should appear. Select the options shown.
- Make sure the
- Click OK to close the window.
- Select Submit from Setup menu. When the calculation is completed you will be notified.
- Under the Display menu, select Properties.
- A window should appear (the values in this example should differ from yours). If there are no values in the window then you need to double click on the molecule.
- Record the dipole moment and energy given. (In this example the dipole = 3.9 debye).
- Calculate the dipole moment for dihedral angles: 0 through 180 degrees in 10 degree increments. (Hint: Just click on the pink bond and change the value in the box.). Do not define a new constraint at this point. This will confuse the program completely!
- For the higher angles (>120 degrees), you might have to uncheck the symmetry box in the setup calculation menu. However, sometimes it is more advisable to approach from 180 degrees going down.
- Plot the dipole moment and energy of benzil vs. the dihedral angle (use MS Excel, XY Scatter plot). Do you see any trends? If so, rationalize this observation.
Part IV: Phase Transfer Oxidation (due in prelab)
1. What is the function of the sodium hypochlorite in this reaction?
2. You are going to use a separatory funnel for the work-up in this week's experiment. Answer the following questions.
a. Why is it important to 'vent' the separatory funnel frequently? Why do you want to make sure not to point the stem towards a different person?
b. Why do you have to remove the stopper on top when you drain the solution out of the sep funnel?
3. Given the following mixture: butanol, methanol and dichloromethane. The GC spectrum is acquired isothermally at 90 oC. Answer the following questions:
a. Determine the sequence of in which they will come out of a GC column with a polar column.
b. What would change (if anything) if non-polar column is used instead ?
c. What would change if the temperature would be descreased by 10 oC?
d. What would change if spectrum is obtained using a temperature gradient of 10 oC/min (starting from 80 oC ending at 100 oC)?
4. Recrystallization
a. Why is it necessary to bring the solvent to a boil in the process of recrystallization?
b. What can you do if no crystals form from the solution?
c. Why do you perform a recrystallization in general?