Meeting 3 Problem Set - 30BL
NO ONLINE QUIZ FOR THIS MEETING!
1.Using PC Spartan 2002 at the Science Learning Center (4th Floor Young Hall) do the following:
a. Draw camphor if you have not done it yet (Make sure that all hydrogen atoms are still attached!). Minimize the structures by clicking the minimize icon, ![]() , then save.
, then save.
b. Go to the view mode by clicking the view icon, ![]() . Once in the view mode, click the Model menu and select Tube.
. Once in the view mode, click the Model menu and select Tube.
c. Select Calculations from the Setup menu.
The following window should appear. Select the options shown.
Verify the Charge is Neutral and Multiplicity is Singlet. Click OK.
- Select Submit from Setup menu.
- Under the Setup menu, select Surfaces. A window should appear. In this window click Add.
A second window should appear. In this window, select the following
Then click OK to exit dialog. Close the previous window.
Select Submit from Setup menu. When the calculation is completed you will be notified.
- Under the Display menu, select Surfaces.
A window should appear. In this window check the yellow box.
Next, select the molecule by clicking on it. In the bottom right corner of the window, change the selection from Solid to Transparent.
d) Do the same (steps a-c) for 2-norbornanone.
2. Referring to the below reaction,
answer the following questions:
a. Which isomer is expected to be the major product for this reaction? Why? (Include the LUMO diagram generated in question 1 to answer this question. Make sure to show the proper orientation! Hint: What are you trying to show here?)
b. What would change if NaBH4 and CH3OD/D2O were used in this reaction? Show the structure of the product.
c. Why is the LUMO orbital used to rationalize the stereochemistry in this reaction?
3. Referring to the below reaction,
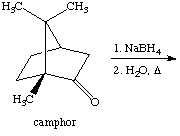
answer the following questions:
a. Draw the products formed in this reaction
b. Which product is the major and which is the minor? Explain using the LUMO generated above (Include the LUMO diagrams generated in question 1 to answer this question. Make sure to show the proper orientation!). What are the differences compared to 2-norboranone?
4. Experimental
a. Why is diethyl ether a poor choice as solvent for the reaction?
b. Why is sodium borohydride used as reducing reagent in the reaction as compared to lithium aluminum hydride?
c. After the reaction is completed, the reaction mixture is chilled and water is added. Which purpose does this step serve?
d. In lecture it was emphasized to minimize the amount of drying agent being used. Explain why. How does the student know that he added enough?
e. How is the solvent removed after the drying step?
f. A student observes a melting point of 205-210 oC for his final product in this reaction. Which conclusion(s) can he draw?
g. Why is it important to submit a fairly dilute sample for the acquisition of the GC?
h. Which information does the student obtain from the GC spectrum?