Problem set #2 (Meeting 2)
ATTN: answers to the below questions are due at the start of meeting 2; these answers should be part of your pre-lab write-up.
1. The reaction mixture of the elimination reaction usually turns dark in color (black, brown, blue, green). Explain briefly why.
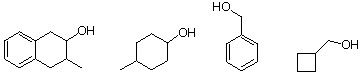
2. What is the expected alkene product formed from the dehydration of the following alcohols? Show major products only. help

3. The reaction of cyclohexene with potassium permanganate affords cis-1,2-cyclohexanediol, while the reaction with bromine yields trans-1,2-dibromocyclohexane. Explain briefly by showing the key intermediates of each reaction.
4. How do you know which layer to keep during the work-up of your reaction mixture in general? Which one is it in this experiment? Explain briefly.
5. What are the most important changes in the IR spectrum going from cyclohexanol to cyclohexene (functional groups and wavenumbers)?
6. In this reaction, two distillations are carried out.
a. The procedure asked for the first distillation to be carried out slowly. Why? What do you distill here?
b. Why is the second distillation performed?
7. Why is it important to optimize the use of the drying agent? How do you know that you have enough drying agent?
8. Using PC Spartan 2002 at the Science Learning Center (4th Floor Young Hall) do the following:
a. Use the alcohols and their protonated forms (CH3CH2-OH, CH3CH2-OH2, (CH3)2CH-OH, (CH3)2CH-OH2, (CH3)3C-OH, (CH3)3C-OH2) that you drew last week for this exercise.
b. Select Calculations from the Setup menu.
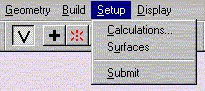
The following window should appear. Select the options shown.
Verify that the Charge is Neutral (for -OH) or Charge is Cation (for -OH2) and Multiplicity is Singlet. Click OK.
Select Submit from Setup menu.

Then click OK to exit dialog. Close the previous window.
Select Submit from Setup menu. When the calculation is completed you will be notified. It should not take more than 2-3 minutes for the calculation to complete under normal circumstances. Make sure that you have only one window open at this point. The messages are usually displayed in the first window, and often not in the window you are working in at this point.
1. Using the distance tool, measure the distance C-O and record it.
2. Under the Display menu, select Properties. Click on the oxygen atom.A new window should appear (atom properties). Record the value for the Natural Charge. Do the same for the C-atom the has the oxygen attached.
Generate two plots (include them in your prelab):
1. The C-O bond distance as a function of the type of alcohol or carbocation (primary, seconday, tertiary) (You should have six points in your graph).
2. Do the same for the natural charge on the oxygen and carbon as a function of the carbocation.
Based on the obtained graphs, answer the following questions:
1. How does an added proton influence the C-O-bond distance in the different molecules? Rationalize the changes.
2. How does it influence the partial charges on the carbon and oxygen?
Problems: Check here