Problem set #2 (Meeting 2)
ATTN: answers to the below questions are due at the start of meeting 2; these answers should be part of your pre-lab write-up. Show pertinent equations where appropriate.
1. Referring to the benzoin condensation, answer the following questions.
a. A student does not read the procedure carefully enough and does not add the 2N NaOH solution to the reaction mixture. What would he observe?
b. The lab support provided benzaldehyde that was placed in an open bottle. Which problem does this pose for this reaction?
c. What is the function of 95% ethanol in the reaction?
d. A student starts off with 0.25 g of thiamine hydrochloride and 1 mL of 0.20 N sodium hydroxide solution. Afterwards, he adds 2.50 mL of benzaldehyde to his solution. After teh work-up, he isolates 2.30 g of benzoin. Determine the yield for the reaction. Show your calculations.
2. Vacuum filtration
a. Draw a sketch for the setup used for the filtration of the benzoin and label all parts needed.
b. Why is it important to use filter paper in this step? How do you determine which type of filter paper is correct and which size is needed?
c. Why has the filter flask to be clamped during the filtration?
d. Why are the crystals rinsed with ice-cold water and ice-cold 95% ethanol?
3. Referring to the elimination reaction, answer the following questions.
a. The procedure asks for two distillations. Which purpose does each distillation serve?
b. Many of the reaction mixtures change color to dark green or blue, or even black. Rationalize this observation.
c. Which compound(s) distill(s) over during the first distillation?
d. The distillate is transferred into another container. How is the crude product isolated from there?
e. What is the function of the saturated sodium chloride solution used during the work-up?
f. How is the IR spectrum for the final product obtained in the lab?
g. Why does the final product have a lower boiling point than the reactants?
4. a. Using PC Spartan 2002, perform the following calculations for the alkenes: terpinolene, limonene, a-terpinene, isoterpinolene. Make sure that all hydrogen atoms are present and there are also no extra ones either.
b. Select Calculations from the Setup menu.

The following window should appear. Select the options shown.
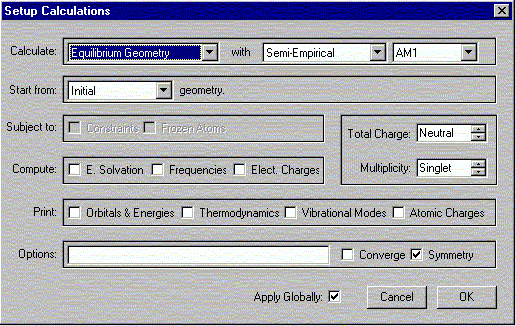
Verify that the Charge is Neutral and Multiplicity is Singlet. Click OK.
Select Submit from Setup menu.

Then click OK to exit dialog. Close the previous window.
Select Submit from Setup menu. When the calculation is completed you will be notified. It should not take more than one minute for the calculation to complete under normal circumstances. Make sure that you have only one window open at this point. The messages are usually displayed in the first window, and often not in the window you are working in at this point.
Under the Display menu, select Properties. Record the value for the Energy.
1. Based in the observed trends in trends in the heat of formation (=energy), which alkene is the most stable and which one is the least stable one? Can you rationalize these observations? Do the obtained data match with your expectation? If not, what is the conclusion?
2. Can you explain the product distribution observed for the elimination of water from a-terpinol (see reader page 20)?
Problems with calculations: Check here