Week 8 Condensed Answer Key
1. a. Water acts an acid when brought in contact with a Grignard reagent, which is a good nucleophile but also also a very strong base. Because the acid-base reaction is much faster than the nucleophilic attack of a carbonyl group, the Grignard reagent would be consumed by the first reaction before the benzoin enters the reaction.
CH3MgBr + H2O ----> CH4 + Mg(OH)Br (R1)
b. The Grignard solution is diluted and placed in an ice-bath during the initial stages because the initial reaction is an acid-base reaction (MeMgBr with the hydroxyl function of benzoin) that is exothermic and also produces a gas, methane. Without the cooling, the solvents (diethyl ether and tetrahydrofuran) would evaporate quickly and many side reactions would be observed as well.
CH3MgBr + ROH ----> CH4 + Mg(OR)Br (R2)
In addition, the reaction can be better controlled and side reactions are reduced as well.
c. Since benzoin is relatively polar, it dissolves rather poorly in diethyl ether requiring a lot of solvent to dissolve the benzoin. Thus, diethyl ether is a poor choice as solvent here.
d. The sulfuric acid serves as proton source in this experiment. It quenches the excess of the Grignard reagent (R3) and also converts the Mg-alcoholate into the diol (R4).
"(O-C-C-O)Mg" + H2SO4 ----> "HO-C-C-OH" + Mg2+ + SO42- (R4)
e. A small amount of the sulfuric acid dissolves in the organic layer. The treatment of the organic layer with sodium bicarbonate removes the acid from the organic layer.
H2SO4 + HCO3- ----> HSO4- + CO2 + H2O (R5)
The crude has to be heated during the removal of the solvent and the recrystallization process. The presence of acid will increase the probability that the compound will undergo an acid-catalyzed dehydration and subsequent rearrangement (see reader).
f. The product dissolves pretty well in THF and diethyl ether. While a small amount of these solvents in the crude product will be acceptable, larger quantities increase the polarity of the organic layer and therefore the solubility of the product. :-(
g. High-boiling petroleum ether is a mixture of hydrocarbons that boils between 90-120 oC. The high-boiling petroleum ether used in the lab is a cheap alternative to heptane or octane.h. At room temperature, benzoin displays a decent solubility in high-boiling petroleum ether. However, its solubility would drop significantly (to 0 oC) causing the bulk of the unreacted benzoin to precipitate if it was present in larger quantities.
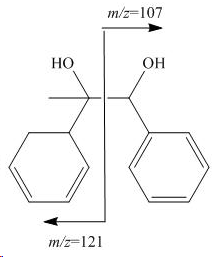
i. The two fragments are formed by the cleavage of the central C-C bond. The left fragment displays an abundance of 80 %, while the fragment on the right displays an abundance of 21 %. The difference in abundance is a direct result of the different stabilities of the resulting cations. The fragment on the left is more stable because of the higher degree of substitution.
