Introduction:
An aldol condensation is a base catalyzed reaction between a pair
of aldehydes or ketones. The mechanism for these reactions are
somewhat complex and will be covered in the lecture course (130A).
However, one can easily determine the final product without understanding
the meachanism. [Understanding the mechanism for these reactions
is important but being able to quickly determine what the final
product looks like should aid you immensly in determining the
mechanism.]
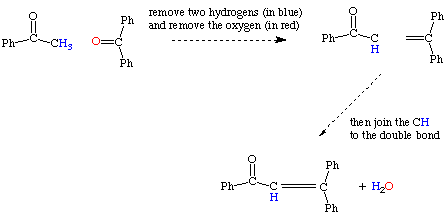
Problem 1a is an example of an aldol condensation with dehydration. Acetophenone and benzophenone are coupled together yielding an unsaturated ketone. Notice that 1 equivalent of water is lost in this reaction (thus we have the dehydration).

Referring to the above reaction, effectively the oxygen (in red) and the alpha hydrogens (in blue) are removed in the form of water. It is importnant to note that Two alpha hydrogens are removed in these type of reactions.
Determining the outcome of an aldol condensation with dehydration is fairly easy if one uses a systematic method. The following diagram demonstrates how this can be done: