updated last
Answer Key Extra Credit Project (DHPM)
1. The reaction does not use a solvent during the reaction and only very little during the purification (ethanol, acetone). Some sunlight is used as heat source because the grinding in the mortar proved to be insufficient for the reaction to occur at a reasonable rate (as described in the literature). The solvent-free condition makes this reaction an environmentally benign procedure because it reduces problems that are associated with the use of large quantities of organic solvents such as safety, cost, waste handling and pollution. In this reaction, only water, ethanol and acetone are used.
2. The p-toluenesulfonic acid (p-CH3C6H4SO3H)
is used as catalyst in the reaction. Initially,
urea and 4-methoxybenzaldehyde undergo an
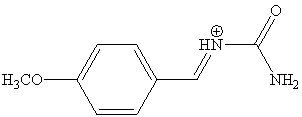
acid-catalyzed formation of a N-acyliminium
ion (shown below). The cation reacts with a CH-acidic compound (via its enol form) to
yield the ureide, which undergoes an acid-catalyzed cyclization and
dehydration to form a racemic mixture of 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)–substitited
3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2-one.

3. The
mixture has to be mixed thoroughly before it is stored in the sunlight
to overcome the barriers associated with solvent-free reactions. Only
part of the urea and the catalyst dissolve in the liquids (ethyl
acetoacetate,
4-methoxybenzaldehyde). The vial has
to be closed well to prevent the oxidation of the benzaldehyde.
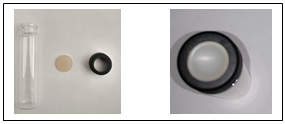
4. A 6-dram vial is used for the reaction. The regular black cap is
replaced by a compression cap and a flat Teflon septum that is pushed
inwards a little (as shown on the right side below).
5. The treatment of the reaction mixture with hot sodium bicarbonate
solution aims to extract the excess of urea, the catalyst
(p-toluenesulfonic acid) and some benzoic acid (formed by oxidation of
the benzaldehyde). The target compound, the aldehyde and the
ethyl acetoacetate are not soluble in water and have to be separated by
recrystallization.
6. The 13C-NMR
spectrum of the compound displays thirteen signals: two carbonyl carbons
(ester, amide, 150-170 ppm), six aromatic/alkene carbons (100-150 ppm), five aliphatic carbons
(10-80 ppm).