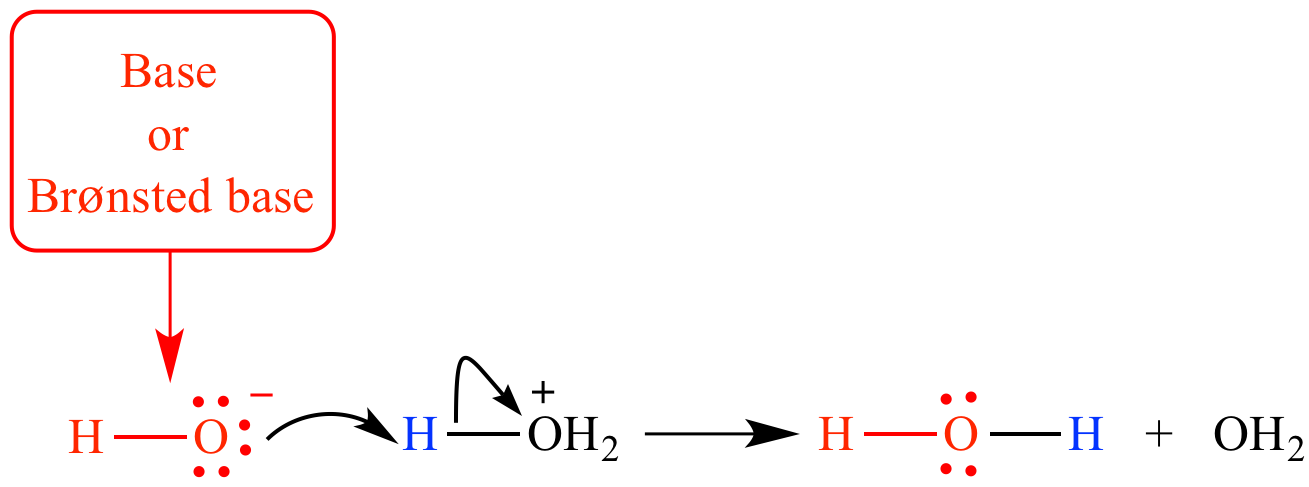
Hydroxide ion is a strong Bronsted base and good nucleophile. When hydroxide ion is under discussion as a proton acceptor (such as in its reaction with hydronium ion) it is called a base or a Bronsted base.

When hydroxide's role as an electron donor to an atom other than hydrogen is being considered (such as its role as a nucleophile in an SN2 reaction), it is called a nucleophile or a Lewis base.